Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the healthcare landscape, sparking both excitement and skepticism. From diagnosing diseases to personalizing treatment plans, AI promises to revolutionize patient care. However, this transformation comes with risks and ethical dilemmas that demand careful consideration.
What is AI in Healthcare?
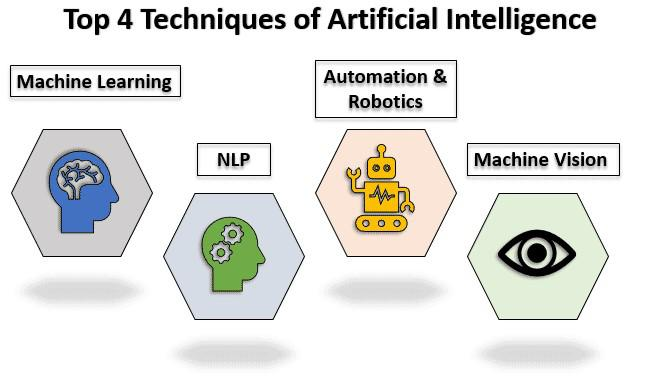
AI in healthcare refers to the use of algorithms and machine learning to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. These tasks range from analyzing medical images to predicting patient outcomes. By leveraging large datasets and computational power, AI can identify patterns and insights that might escape even the most skilled professionals.
For instance, AI-powered tools like IBM Watson and Google DeepMind’s healthcare projects have demonstrated remarkable success in diagnosing diseases such as cancer and diabetes. These tools process vast amounts of medical data within seconds, making them invaluable in time-sensitive scenarios.
Related:
● The Future of AI in Primary Care: Will it Replace Family Doctors?
● Can AI-Powered Chatbots Replace Human Medical Advice?
● AI in Healthcare: How Real is the Risk of Over-Reliance?
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
The advantages of AI in healthcare are undeniable. One of its most compelling features is accuracy. Algorithms trained on thousands of medical cases can identify subtle anomalies in diagnostic imaging, often outperforming human experts. This capability is particularly significant in detecting early-stage cancers, where timely intervention can save lives.
AI also enhances efficiency. Automated systems streamline administrative tasks like scheduling, billing, and patient documentation. This allows healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care rather than clerical duties.
Another key benefit is personalized medicine. AI can analyze genetic information, lifestyle habits, and medical history to create tailored treatment plans. For example, pharmacogenomics—the study of how genes affect drug response—is now more accessible thanks to AI’s analytical capabilities.
Risks and Challenges
Despite its potential, AI in healthcare is not without flaws. One of the primary concerns is data privacy. Medical data is highly sensitive, and breaches can have devastating consequences. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect patient information from unauthorized access.
Another challenge lies in algorithm bias. AI systems learn from historical data, which can sometimes reflect societal biases. For instance, a diagnostic tool trained on predominantly Caucasian patient data might underperform for other ethnic groups. Such biases could exacerbate healthcare disparities rather than mitigate them.
Moreover, over-reliance on AI poses risks. While machines excel at pattern recognition, they lack the contextual understanding and empathy that human doctors provide. Misdiagnoses or incorrect treatment recommendations due to algorithm errors could have severe consequences.
MORE STORIES FROM THE TECH ABC:
● Apple ID Scam? The Dumbest Thing People Still Fall For!
● What Are the Hidden Dangers of Storing Money in Payment Apps?
● How to Extend iPhone Battery Life in 2025?
Ethical Considerations

The integration of AI in healthcare raises profound ethical questions. Should AI have the authority to make life-or-death decisions? How do we hold an algorithm accountable for errors? These dilemmas require clear regulatory frameworks to ensure ethical AI deployment.
Additionally, there is the issue of patient consent. Many patients may not fully understand how their data is used by AI systems. Transparent communication is critical to building trust and ensuring informed consent.
Real-World Applications
AI is already making waves in healthcare. For example, radiology departments use AI to analyze X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs with remarkable speed and precision. Similarly, AI chatbots assist in triaging patients by answering basic health queries and guiding them to appropriate care.
In surgery, robotic systems like da Vinci combine AI with advanced robotics to perform minimally invasive procedures. These systems enhance precision, reduce recovery times, and improve patient outcomes.
AI is also transforming drug discovery. Traditional pharmaceutical research is costly and time-consuming, but AI accelerates the process by identifying potential compounds and predicting their effectiveness. This has proven especially valuable in developing vaccines and treatments during global health crises.
- 50 Years Later, Gates Shares the Code That Built Microsoft

- RTX 5090 Cables Melting—Is Your GPU at Risk?

- ChatGPT Overload! When Does Daily Use Turn Into Addiction?

- Switch 2 Leak: Why It’ll Crush PS5 & Xbox from Day One!

- PS5 Pro vs. PS5: 4K Dreams or Marketing Scheme?

- Assassin’s Creed Shadows Stuns, But Is PS5 Pro Wasted?

The Future of AI in Healthcare
As AI continues to evolve, its potential applications in healthcare are virtually limitless. Predictive analytics could help identify at-risk populations and prevent diseases before they occur. Wearable devices integrated with AI could monitor patients’ vital signs in real time, alerting doctors to any abnormalities.
However, achieving these advancements requires collaboration between technologists, healthcare providers, and policymakers. Standardized regulations, ethical guidelines, and ongoing education are crucial to ensuring that AI benefits all patients equally.
Conclusion
AI in healthcare is undoubtedly a game-changer, offering unparalleled opportunities to improve diagnostics, treatment, and efficiency. Yet, it is also a risky experiment, fraught with challenges and uncertainties. Balancing innovation with caution is essential to harness the full potential of AI while safeguarding patient well-being. By addressing ethical concerns and prioritizing transparency, we can navigate this transformative era responsibly.