Artificial intelligence (AI) is making inroads into primary care, raising questions about its future role. Tasks like diagnosing common ailments, recommending treatments, and managing patient records are already seeing AI-driven innovations. But will these technologies eventually replace family doctors?
AI’s Expanding Role in Primary Care
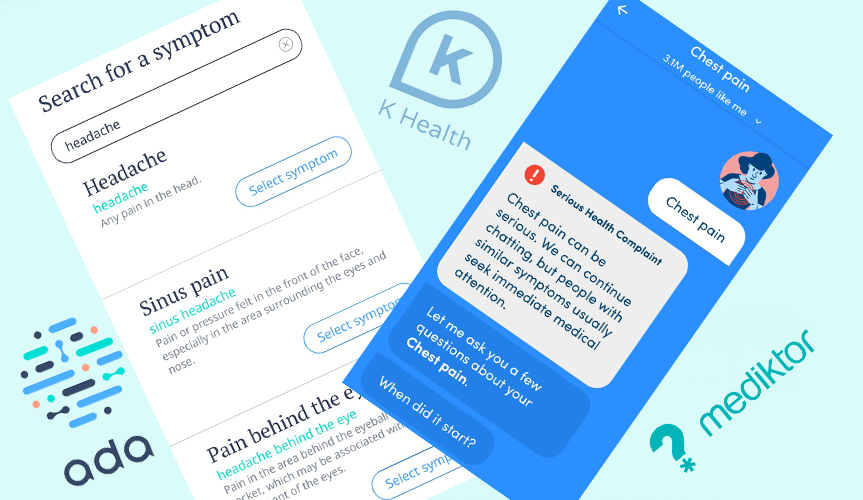
AI in primary care involves using algorithms and machine learning to enhance routine healthcare tasks. These tasks range from managing administrative workflows to diagnosing illnesses through patient data analysis. AI tools like symptom-checking apps and predictive analytics software are becoming integral in many clinics worldwide.
For example, platforms such as Babylon Health analyze symptoms to suggest possible conditions, while wearable devices track vital signs to flag early health concerns. These innovations streamline care, allowing doctors to focus on more complex cases.
The Benefits AI Brings to Clinics
One significant advantage of AI in primary care is its ability to handle repetitive tasks efficiently. By automating scheduling, billing, and documentation, clinics save time and reduce administrative burdens. AI-powered systems also enhance diagnostic accuracy, often outperforming human doctors in detecting early signs of chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
Another notable benefit is accessibility. Virtual assistants and chatbots provide basic healthcare guidance, particularly in underserved areas. Patients can receive preliminary consultations through apps, reducing the strain on overburdened healthcare systems.
Personalized care is another strength. AI analyzes patient data—from genetics to lifestyle habits—to create tailored treatment plans. This enables more precise medication prescriptions and health advice, improving outcomes for individual patients.
Challenges That Limit AI’s Reach
Despite these benefits, AI faces limitations that prevent it from fully replacing human doctors. One major hurdle is its lack of empathy. Family doctors play a critical role in building trust and providing emotional support—qualities machines cannot replicate. A doctor’s ability to interpret subtle cues, like body language or tone of voice, remains unmatched by any algorithm.
Data privacy is another significant concern. AI systems require vast amounts of patient data to function effectively, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. Ensuring data security is paramount to maintain patient trust.
Additionally, AI tools often struggle with complexity. While they excel at identifying patterns in structured data, they may falter when dealing with ambiguous or rare cases. Misdiagnoses due to algorithmic errors could lead to serious consequences.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
The integration of AI in primary care raises ethical and regulatory challenges. For instance, who is responsible if an AI system makes a harmful recommendation? Clear guidelines are essential to define accountability and ensure patient safety.
Regulations also need to address algorithm bias. AI systems can inadvertently reflect biases present in their training data, leading to disparities in care. Developers must prioritize diversity and fairness when designing these tools.
The Synergy Between AI and Family Doctors
Rather than replacing family doctors, AI is more likely to augment their capabilities. By handling routine tasks, AI allows doctors to spend more time on personalized care. For example, AI can pre-screen patients and provide preliminary diagnoses, leaving doctors to focus on nuanced decision-making and treatment planning.
This collaborative approach can also improve efficiency. Doctors equipped with AI tools can access detailed patient insights instantly, enabling quicker and more accurate diagnoses. Such synergy enhances the overall quality of care.
Looking Ahead: AI’s Future in Primary Care
The future of AI in primary care is promising but requires balanced implementation. Wearable devices, remote monitoring systems, and telemedicine platforms integrated with AI are set to play a crucial role. These technologies will empower patients to take charge of their health while keeping doctors informed about real-time changes.
However, to unlock AI’s full potential, collaboration between healthcare providers, technologists, and policymakers is vital. Standardized guidelines, ethical considerations, and ongoing education for medical professionals will ensure AI remains a tool for empowerment rather than replacement.
Conclusion
AI in primary care is a groundbreaking development, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve efficiency and accessibility. While it cannot replace the human touch of family doctors, it serves as a powerful ally. By embracing this technology wisely, the healthcare system can strike a balance between innovation and empathy, ensuring better outcomes for all patients.