When it comes to premium smartphones, Apple’s iPhone lineup has always set a high standard, not just for performance and design but also for the materials used in their construction. With the iPhone 17 on the horizon, speculation about its build materials is heating up. Will Apple stick with the recently introduced titanium or venture into uncharted territory with even more advanced materials?
The Shift to Titanium: A Game-Changer

The iPhone 15 Pro series marked Apple’s transition from stainless steel to titanium for its frame. Titanium’s lightweight nature, combined with its impressive strength, offered tangible benefits. The devices felt noticeably lighter without compromising durability, a crucial factor for users seeking a balance between aesthetics and practicality.

Titanium also brought improved resistance to corrosion and scratches compared to stainless steel. Its premium look and feel aligned perfectly with Apple’s ethos of combining functionality with luxury. However, titanium is not without its drawbacks. It is expensive to source and challenging to work with, which could explain the limited application to the Pro models rather than the entire lineup.
Exploring Alternatives: What Lies Ahead?
While titanium has proven its merit, Apple’s relentless pursuit of innovation could lead them to explore other materials for the iPhone 17. Here are some contenders:
- Carbon Fiber Composites Carbon fiber is lightweight, strong, and highly customizable. Its use in industries like aerospace and automotive underscores its potential as a premium smartphone material. A carbon fiber iPhone could further reduce weight while maintaining durability. However, challenges like high production costs and potential interference with wireless signals might limit its viability.
- Liquidmetal Liquidmetal, an amorphous alloy, has been in Apple’s portfolio for years. Known for its incredible strength, elasticity, and resistance to wear, Liquidmetal could offer a futuristic aesthetic and superior durability. Although it has primarily been used in small components like SIM ejector tools, scaling it up for an iPhone’s frame might finally become feasible.
- Ceramic Ceramic materials, such as those used in the Apple Watch Edition, offer unparalleled scratch resistance and a smooth, premium finish. A ceramic iPhone could appeal to users prioritizing aesthetics. However, ceramic is brittle, which could raise concerns about impact resistance.
- Recycled Aluminum Alloys Apple’s commitment to sustainability could lead to the reintroduction of aluminum in a more eco-friendly form. Recycled aluminum alloys are lightweight, durable, and easier to mass-produce than titanium or carbon fiber. Pairing recycled materials with innovative coatings might deliver a fresh look without compromising performance.
Design Implications of Material Choices
Material choices directly influence the design and functionality of an iPhone. For instance, titanium’s adoption allowed for thinner bezels and a lighter frame, enhancing user experience. A switch to carbon fiber or Liquidmetal could open new design possibilities, like increased flexibility or even modular components.
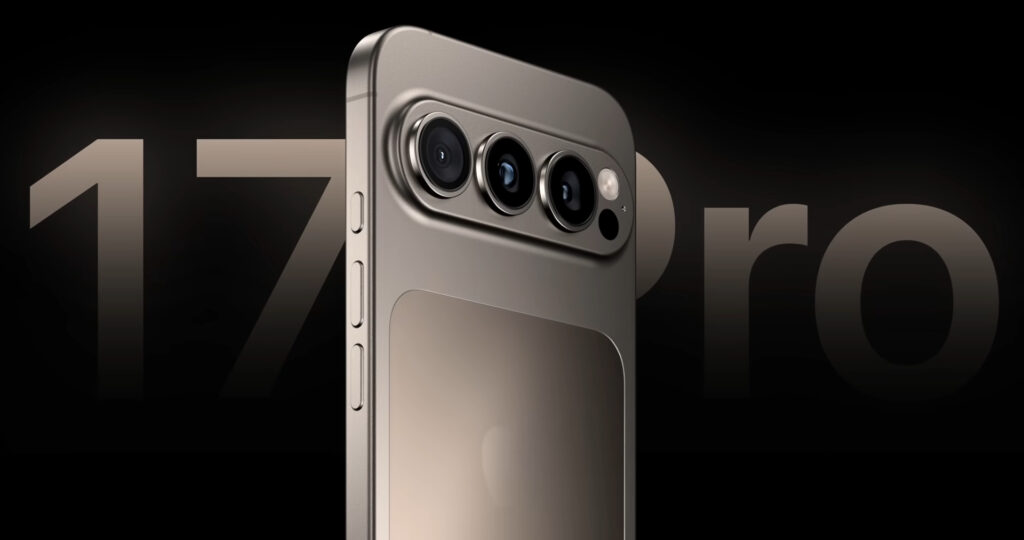

Apple’s focus on tactile quality and visual appeal ensures that any material used must resonate with its design philosophy. Advanced materials might also enable better thermal management, a growing concern as smartphones become more powerful.
Sustainability: A Driving Force
Sustainability remains central to Apple’s strategy. The company’s goal to achieve carbon neutrality by 2030 has already influenced the materials used in its products. Recycled and renewable materials are increasingly prioritized, evident in the aluminum enclosures of MacBooks and iPads.
For the iPhone 17, Apple might integrate recycled titanium or explore bio-based polymers for non-structural components. Such initiatives not only reduce environmental impact but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Consumer Expectations and Industry Trends
Consumer demand for premium materials continues to rise, with users valuing durability, weight, and aesthetics. Meanwhile, competitors like Samsung and Google are also experimenting with unique materials, adding pressure on Apple to stay ahead.
Foldable phones, for instance, rely on flexible materials like ultra-thin glass and advanced polymers. While Apple has yet to release a foldable device, the iPhone 17’s material choices could hint at the company’s future direction in this space.
Balancing Cost and Innovation
Premium materials come at a price, and Apple must strike a balance between innovation and affordability. Titanium’s inclusion in the Pro models exemplifies this strategy. For the iPhone 17, Apple might reserve advanced materials for higher-end models while using cost-effective alternatives like recycled aluminum for standard versions.
Conclusion: Titanium or Beyond?
The iPhone 17’s build materials will reflect Apple’s ongoing quest for innovation, sustainability, and user satisfaction. While titanium remains a strong contender, emerging materials like carbon fiber, Liquidmetal, or recycled alloys could redefine the smartphone’s form and function.
Apple’s ability to seamlessly blend cutting-edge materials with its iconic design ethos ensures that the iPhone 17 will set a new benchmark, whether it sticks with titanium or ventures beyond. Whatever the choice, one thing is certain: the iPhone 17 will continue to embody Apple’s commitment to quality and innovation.