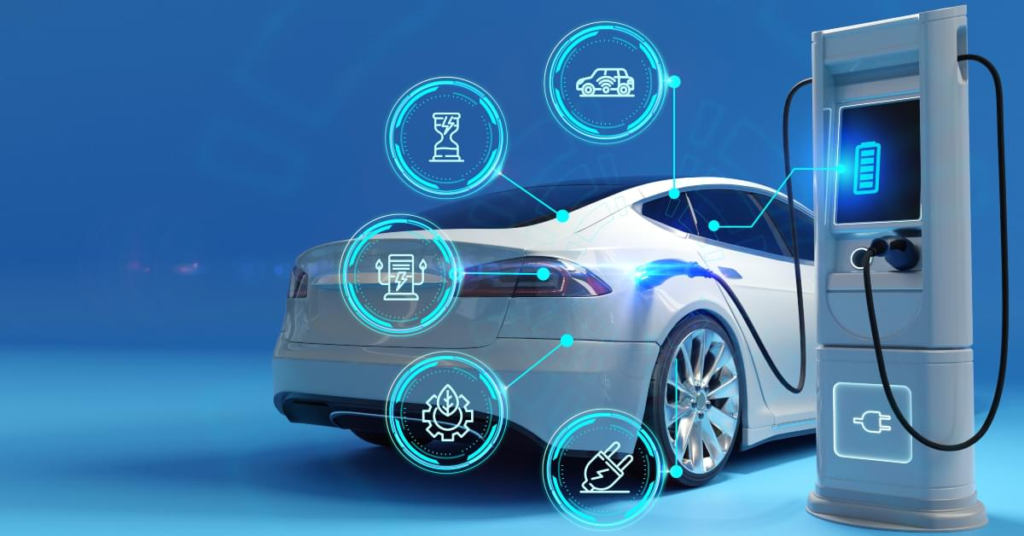
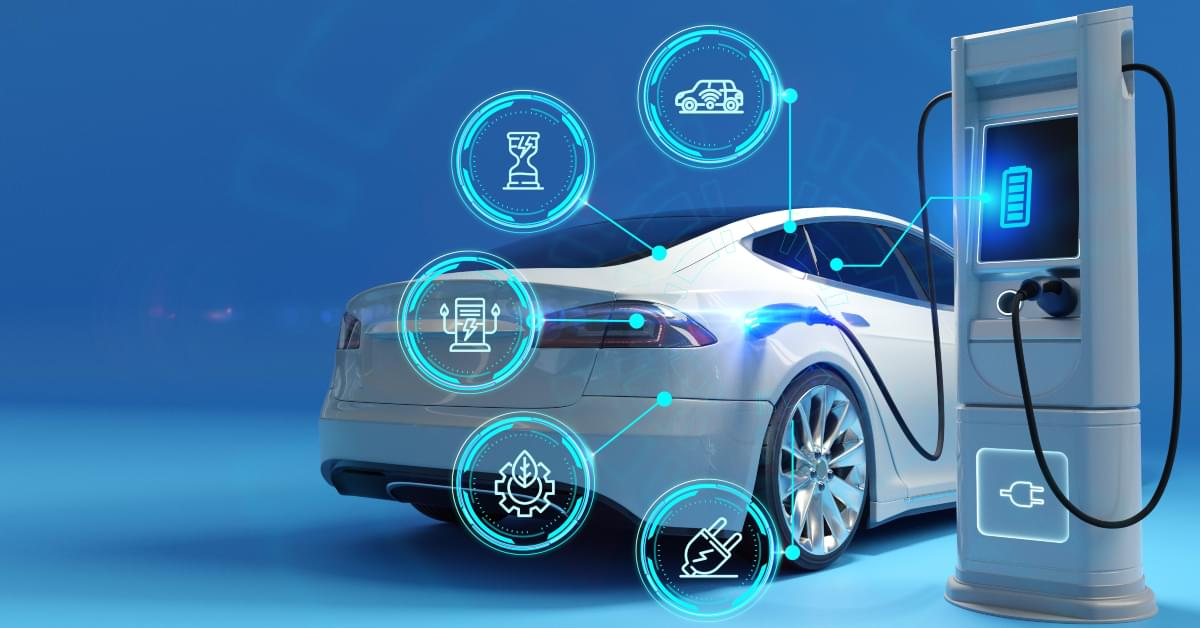
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become a symbol of progress in modern transportation, blending efficiency, sustainability, and advanced technology. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, the adoption of EVs is reshaping the automotive landscape. This article delves into the essence of electric vehicles, their impact on society, and why they represent the future of driving.
Follow Us On Whatsapp
What Is an Electric Vehicle (EV)?
An electric vehicle is powered by electricity rather than traditional fossil fuels like petrol or diesel. Unlike internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, EVs use an electric motor, drawing energy from a rechargeable battery. These vehicles are categorized into three types:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): Fully electric, with no reliance on fossil fuels. Examples include the Tesla Model 3 and Nissan Leaf.
- Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): Combine a battery-powered motor with a traditional engine, offering flexibility for longer trips.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Powered by both an electric motor and an ICE but do not require external charging.
Key Components of Electric Vehicles
EVs consist of advanced components that distinguish them from traditional vehicles:
- Battery Pack: Typically lithium-ion, providing energy storage for the motor.
- Electric Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the wheels.
- Power Electronics Controller: Regulates the flow of electricity from the battery to the motor.
- Charging System: Allows the vehicle to recharge via standard outlets or fast-charging stations.
Why Are EVs Gaining Popularity?
The rise in EV adoption can be attributed to several factors, including environmental benefits, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences.
Environmental Benefits
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution. By relying on renewable energy sources for charging, the carbon footprint of EVs can be minimized further. Cities with dense populations benefit immensely from the reduced noise and cleaner air.
Cost Efficiency
Although the upfront cost of EVs can be higher, their long-term savings are compelling. With fewer moving parts, EVs have lower maintenance requirements. Additionally, electricity as a fuel source is more cost-effective than petrol or diesel.
Government Incentives
Many governments offer incentives like tax credits, reduced registration fees, and rebates to promote EV adoption. Policies aimed at phasing out ICE vehicles further boost the appeal of electric alternatives.
Advanced Technology
EVs are often equipped with cutting-edge features such as autonomous driving, over-the-air updates, and advanced infotainment systems. These technologies enhance the driving experience, making EVs a desirable choice for tech enthusiasts.
Challenges Facing EV Adoption
Despite their advantages, EVs face several challenges that require attention:
- Charging Infrastructure: The availability of charging stations remains uneven, particularly in developing regions.
- Battery Longevity and Recycling: Lithium-ion batteries degrade over time and pose environmental concerns if not recycled properly.
- High Initial Costs: While prices are declining, EVs can still be out of reach for many consumers.
The Future of EVs
Electric vehicles are evolving rapidly, with innovations aimed at addressing current challenges and improving performance. Solid-state batteries, wireless charging, and enhanced autonomous capabilities are set to redefine the EV experience. Governments and private enterprises are investing heavily in building charging networks and developing renewable energy solutions.
Global Trends in Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption
The global EV market is expanding, with countries like Norway, China, and the Netherlands leading the charge. In Pakistan and India, EV adoption is on the rise, driven by government initiatives and increasing awareness. Affordable models tailored to these markets are key to further penetration.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles (EVs) are more than just an alternative to traditional cars; they represent a shift toward a sustainable and technologically advanced future. With ongoing innovations and increasing support from governments and industries, EVs are set to become the norm rather than the exception. For individuals and businesses alike, embracing EVs is not just an environmentally conscious decision but a step toward redefining the way we think about transportation.