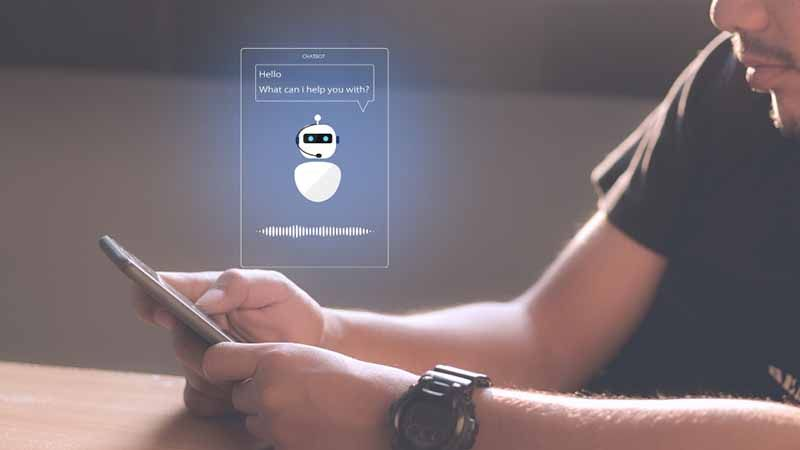
AI-powered chatbots are transforming the way people access medical advice. By leveraging artificial intelligence, these chatbots provide users with instant responses to health-related queries. But how effective are they compared to human doctors, and can they ever truly replace human medical advice?
How AI-Powered Chatbots Work

AI-powered chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand user input and generate appropriate responses. They are designed to simulate human-like conversations, making them accessible and intuitive for users. These chatbots can answer questions about symptoms, suggest possible diagnoses, and recommend next steps, such as seeing a specialist or visiting an emergency room.
For example, tools like Healthily and Ada Health have gained popularity for their ability to provide preliminary health assessments. Users input symptoms, and the chatbot generates potential causes and guidance based on its database of medical knowledge.
Benefits of AI Chatbots in Healthcare
One of the most significant advantages of AI chatbots is accessibility. They operate 24/7, offering immediate assistance without the need for appointments. This feature is particularly valuable in remote or underserved areas where healthcare professionals may be scarce.
[RELATED: AI in Healthcare: How Real is the Risk of Over-Reliance?]
Chatbots also help alleviate the workload of medical staff by handling routine inquiries. For example, they can provide information about medications, explain post-operative care instructions, or answer general health questions, freeing up doctors and nurses for more complex tasks.
Additionally, AI-powered chatbots promote patient engagement. By encouraging users to track symptoms and seek timely medical advice, these tools empower individuals to take charge of their health.
Limitations and Risks
Despite their advantages, AI chatbots have notable limitations. One major issue is accuracy. While chatbots can analyze symptoms and provide general advice, they lack the nuanced understanding of a human doctor. Complex or ambiguous cases often require a level of clinical judgment that AI cannot replicate.
Another concern is data privacy. Chatbots process sensitive health information, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. Robust encryption and strict data policies are essential to protect user confidentiality.
Moreover, chatbots are prone to errors if their underlying algorithms are flawed or biased. For example, a chatbot trained on data from specific demographics may fail to provide accurate advice for individuals outside that group. Such biases could exacerbate health disparities rather than reduce them.
Ethical and Emotional Factors
AI-powered chatbots lack empathy, a critical component of medical care. Human doctors provide emotional support and reassurance, especially during difficult diagnoses or treatments. Chatbots, while efficient, cannot replicate this human connection.
Ethical concerns also arise around accountability. If a chatbot provides incorrect advice that leads to harm, determining responsibility becomes challenging. Clear guidelines are necessary to address such scenarios and establish boundaries for chatbot usage.
A Complement, Not a Replacement
Rather than replacing human doctors, AI-powered chatbots are best viewed as complementary tools. They excel at providing quick, general information and triaging cases, directing users to appropriate healthcare resources. For instance, a chatbot can recommend visiting a doctor based on symptom severity, ensuring timely intervention.
Doctors, in turn, can use chatbots to gather preliminary information before consultations, saving time and enhancing efficiency. This collaboration between humans and AI has the potential to improve healthcare delivery without compromising quality.
The Future of AI Chatbots in Healthcare
As technology evolves, AI-powered chatbots will likely become more sophisticated. Integration with wearable devices and electronic health records (EHRs) could enable real-time monitoring and personalized advice. For instance, a chatbot connected to a fitness tracker might alert a user to potential health risks based on activity patterns or vital signs.
However, achieving this vision requires careful development and regulation. Stakeholders, including technologists, healthcare providers, and policymakers, must work together to address ethical, technical, and practical challenges.
Conclusion
AI-powered chatbots are reshaping the healthcare landscape, offering convenience and efficiency. While they cannot replace the expertise and empathy of human doctors, they serve as valuable allies in managing routine inquiries and promoting patient engagement. By leveraging this technology wisely, we can enhance access to medical advice while maintaining high standards of care.